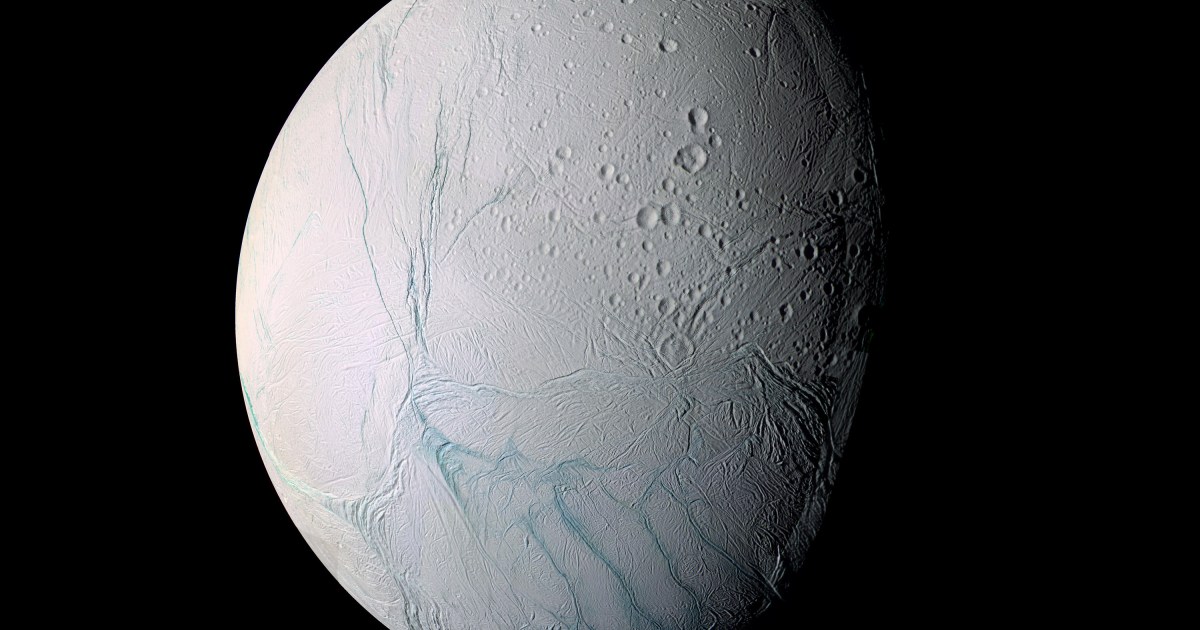
The research used data from the Cassini mission, which performed multiple flybys of Enceladus in the mid-2000s, investigating the water plumes and cryovolcanoes that dot its surface.
“We previously found that Enceladus’ ocean is rich in a variety of organic compounds,” said lead researcher Frank Postberg of Germany’s Freie Universität Berlin in a statement .
No comments:
Post a Comment