 More details: Visit website
More details: Visit websiteIn The News:
Scientists use XRISM spacecraft to predict fate of matter around monster supermassive black hole...Black hole week is in full swing at this point, and to celebrate, NASA has released stunning observations of the heart of a distant spiral galaxy ⁘ as well as the monster supermassive black hole that dwells in that heart.
The observations were conducted by the X-ray Imaging and Spectroscopy Mission (XRISM), led by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) with contributions from NASA; they show the center of spiral galaxy NGC 4151.
This galaxy, located some 43 million light-years away (as well as its incumbent supermassive black hole , which is estimated to have as much mass as 20 million suns) is seen in vibrant reds and bright blues thanks to the addition of radio waves. That addition comes via data from the Very Large Array (VLA) and the Isaac Newton Group of Telescopes.

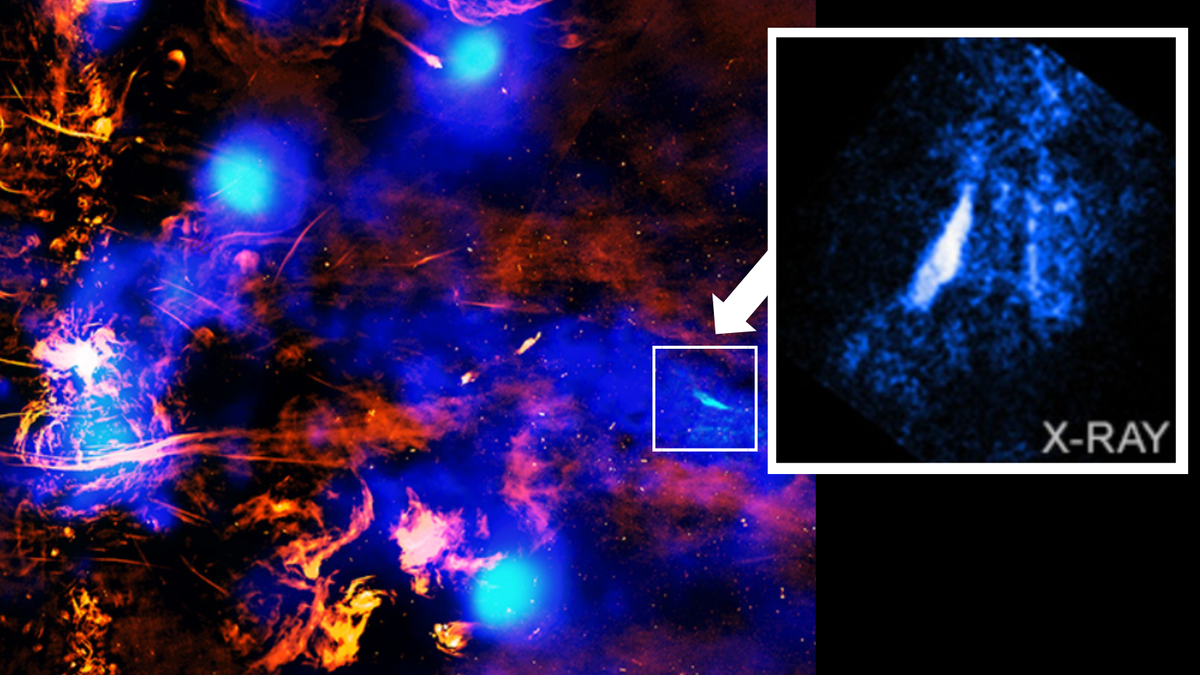
Using NASA's Chandra X-ray space telescope, scientists have discovered a new cosmic "exhaust vent" funneling hot gas away from Sagittarius A* (Sgr A*), the supermassive black hole that sits at the very heart of our Milky Way galaxy.
The newly discovered vent is linked to a chimney-like formation orientated at a right angle in the Milky Way 's disk. The Chandra observation reveals how a "tunnel" at the center of our galaxy helps channel matter to its outer regions.
Many supermassive black holes across the universe are voracious consumers of gas and dust, and even stars, around them. The supermassive black hole at the heart of the Milky Way, Sgr A*, on the other hand, is a light eater. It consumes so little matter, in fact, that if it were a human, it would sustain itself on about one grain of rice every one million years. The Chandra observations could reveal how this cosmic picky eater selects some matter to consume and rejects other material.
Related: New view of the supermassive black hole at the heart of the Milky Way hints at an exciting hidden feature (image)
The vent discovered in X-ray observations of the Galactic Center by Chandra is located around 700 light-years from the region's exact central area, and at the top of the "chimney." This chimney was previously discovered using the European Space Agency (ESA) XMM-Newton , which, like Chandra, observes the universe in X-rays.
The new vent can be seen at the top of the image as a bright blue and white scar against darker blue gas.
No comments:
Post a Comment