
New studies, missions and rich data about asteroids are giving scientists a sharper picture of the solar system's history.
Driving the news: A trio of papers published today analyzed samples from the asteroid Ryugu returned to Earth in 2020 by the Hayabusa2 spacecraft.
Otford Solar System – Otford, England - Atlas Obscura

The Otford Solar System is a scale model built in 1999 to celebrate the new millennium. The scale is 1:4,595,700,000, so one millimeter is equivalent to 4,595.7 kilometers. All the planets of our Solar System are located in their relative positions at midnight on January 1, 2000.
The Webb Space Telescope Sees a Solar System's Beginning - The Atlantic
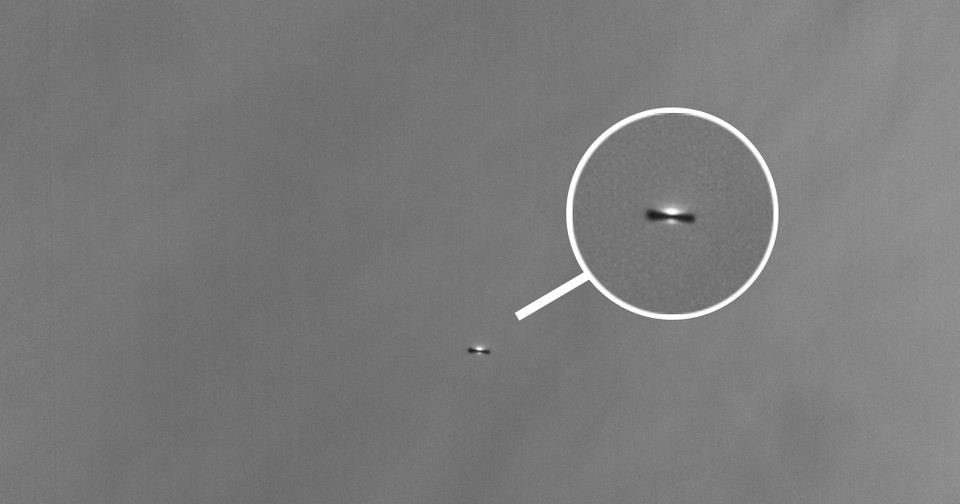
If alien astronomers observed our solar system from a distance 4.5 billion years ago, they would have seen a star surrounded by primordial gas and dust. That material, arranged in a narrow but dense disk, whirled round and round the young star. Over time, its particles collided and formed clumps.
30039 near-Earth asteroids discovered in the solar system

Thanks to Gaia, astronomers got to know more about stars in the galaxy, which act as a backdrop to asteroid observations. These background stars help unravel the asteroid’s positions: the better one knows where the stars are, the more precisely the orbits of asteroids can be computed.
Meet Haumea, the strangest dwarf planet of them all | Popular Science
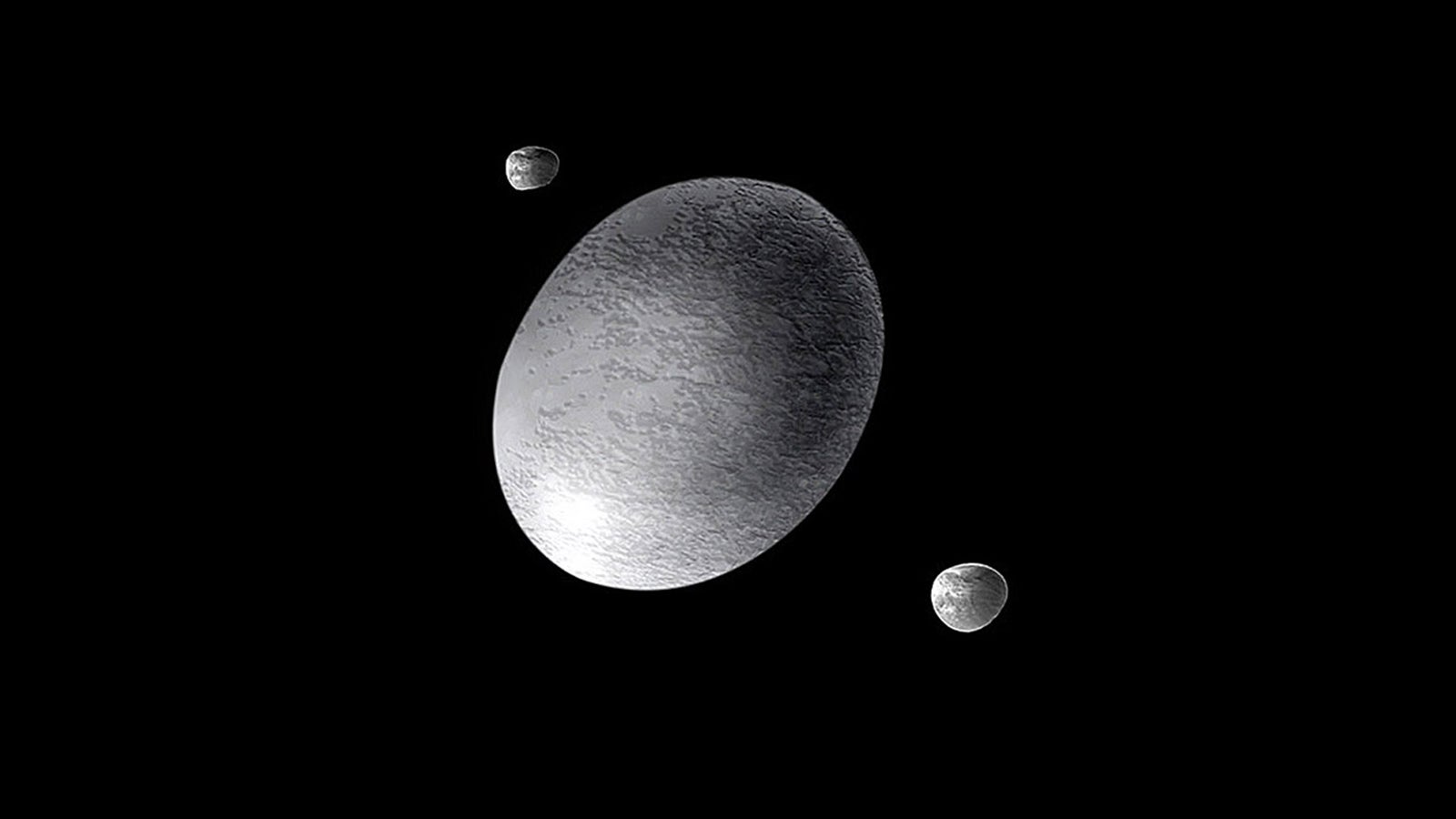

The Kuiper Belt, the donut-shaped ring of icy bodies that stretches far beyond Neptune's orbit, is home to some of the strangest objects in our solar system.
Though it was discovered less than two decades ago, information about the dwarf planet is sparse as Earth-based telescopes have a hard time making precise measurements because of how distant it is. But the little we do know about Haumea suggests that it is an extremely strange and important ...
Angrite Meteorites as Fragments of First-Generation Planetesimals in the Early Solar System | ...
Angrites are olivine-bearing, basaltic meteorites that originate from a volatile-depleted planetesimal.
François Tissot from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and his team carried out a series of crystallization experiments under varying conditions and compared their results with previous petrologic data for the 37 known angrite specimens to better understand their crystallization history.
Rock scooped off speeding asteroid may be comet that lost its tail | University of Chicago News

An analysis of rock scooped directly from the surface of an asteroid by a Japanese spacecraft suggests that it was once a comet that lost its tail.
If confirmed, the finding has implications for our understanding of the early solar system and how the planets and asteroids ended up where they are today.
Starke County unveils solar system model on hiking and biking trail
/cloudfront-us-east-1.images.arcpublishing.com/gray/4GX5AZBALRDKHKNZRYJ7HCMZ7I.bmp)
The Constellation of Starke Creatives Network and Prairie Trails Club welcomed the public to the unveiling of the 'Our Solar System in Scale' project.
Starting at the Erie Trail just east of the Hoosier Valley Rail Museum in North Judson, the OSSIS Installation depicts the planets in our solar system down to a scale of 1:355 million.
SSERVI-sponsored Schmitt-Cernan-Evans Travel Awards | Solar System Exploration Research Virtual ...

The Solar System Exploration Research Virtual Institute is proud to announce the recipients of the Schmitt–Cernan–Evans Travel Grant for students and early career professionals.
For more information about the ANGSA meeting visit: https://www.hou.usra.edu/meetings/ANGSAApollo17_2022/ .
[Press Release] Volatile analysis of the Hayausa2 asteroid Ryugu sample revealing volatile sources and recent surfa… https://t.co/K3RshrKZRd JAXA_en (from Chofu-City, Tokyo) Fri Oct 21 00:56:24 +0000 2022
.@NASA - 1 Asteroid - 0 After a very successful DART Mission, @WHOSTP alongside various agencies received a bri… https://t.co/szB3nO0yxg WHOSTP (from Washington, DC) Tue Oct 18 21:19:01 +0000 2022
Army of the Alien Monkeys
Earth is nice. We want it.
We welcome your submission to us.

No comments:
Post a Comment