
The Milky Way is home to hundreds of billions of stars, and many more planets. Some come in sets, as in our own solar system. But not every planet orbits a star.
The term rogue planet suggests that these objects desert their stars on purpose, striking out on their own to carve a new path through the Milky Way. In reality, rogue planets are usually kicked out of their star system, banished to a solitary existence circling the center of the galaxy.
Not to change the topic here:
Your Guide to Neptune | The Planetary Society
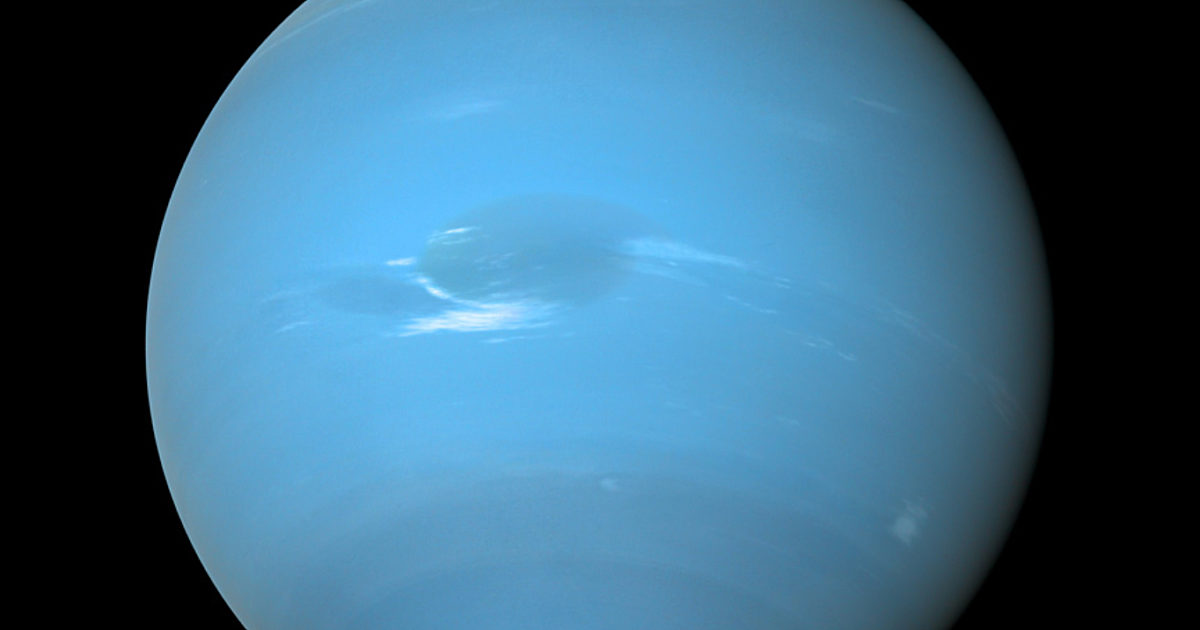
Neptune, along with its cousin Uranus, is the least-explored planet in our solar system, having been visited by a spacecraft only once. Yet we've found more Neptune-sized worlds orbiting other stars than any other type of planet . In order to understand other solar systems and figure out whether our own is unique, we need to learn more about the windy blue world in our own backyard.
Like Jupiter and Saturn , Neptune's atmosphere consists mostly of hydrogen and helium, but it also has methane that absorbs red light, giving it a deep blue hue. Beneath the atmosphere lies an ocean of water, ammonia, and methane, squeezed by intense pressures into a semi-solid state. For this reason we call Neptune an ice giant, though the ice isn't anything like what you'd find in your freezer, with temperatures likely reaching thousands of degrees!
Astronomers discover activity on distant planetary object

A team of astronomers, led by doctoral student and Presidential Fellow Colin Chandler in Northern Arizona University's Astronomy and Planetary Science Ph.D. program, earlier this year announced their discovery of activity emanating from Centaur 2014 OG392, a planetary object first found in 2014. They published their findings in a paper in The Astrophysical Journal Letters , "Cometary Activity Discovered on a Distant Centaur: A Nonaqueous Sublimation Mechanism.
The team's research involved developing a database search algorithm to locate archival images of the Centaur as well as a follow-up observational campaign.
Where were Jupiter and Saturn born?
![]()
New work led by Carnegie's Matt Clement reveals the likely original locations of Saturn and Jupiter. These findings refine our understanding of the forces that determined our Solar System's unusual architecture, including the ejection of an additional planet between Saturn and Uranus, ensuring that only small, rocky planets, like Earth, formed inward of Jupiter.
In its youth, our Sun was surrounded by a rotating disk of gas and dust from which the planets were born. The orbits of early formed planets were thought to be initially close-packed and circular, but gravitational interactions between the larger objects perturbed the arrangement and caused the baby giant planets to rapidly reshuffle, creating the configuration we see today.
This may worth something:
In the hunt for Planet Nine, astronomers eye a new search technique for the elusive world | Space

Astronomers are vetting a "shifting and stacking" technique that could aid the hunt for the putative world, which some researchers think lurks undiscovered in the far outer system , way beyond Pluto's orbit.
The strategy involves shifting space-telescope images along sets of possible orbital paths, then stacking the photos together to combine their light. The technique has already been used to discover some moons in our solar system, and it could potentially spot Planet Nine — also known as Planet X, Giant Planet Five or Planet Next — and other extremely farflung objects, researchers said.
Lighting a path to find Planet Nine | Space | EarthSky

The search for Planet Nine – a hypothesized 9th planet in our solar system – may come down to pinpointing the faintest orbital trails in an incredibly dark corner of space.
An artist's depiction of the hypothesized Planet Nine. Image via Yale University / © stock.adobe.com.
In the search for Planet Nine – a hypothesized ninth planet in our solar system – two Yale astronomers are using a new technique that scoops up scattered light from thousands of space telescope images and identifies a trail of orbital pathways for previously undetected objects in an incredibly dark corner of space, 12 to 23 times farther from the sun than Pluto.
How many habitable planets are out there?

The Drake Equation is a probabilistic argument that details the factors to consider when estimating the potential number of technologically advanced civilizations in the galaxy that could be detected. The Drake Equation is also often considered to be a roadmap for astrobiology and guides much of the research at the SETI Institute.
To develop a reasonable estimate, the researchers looked at exoplanets similar in size to Earth and thus most likely to be rocky planets. They also looked at so-called Sun-like stars , around the same age as our Sun and approximately the same temperature. Another consideration for habitability is whether the planet could have the conditions necessary to support liquid water.
First Habitable-Zone, Earth-Sized Exoplanet Discovered With Planet-Hunter TESS

TOI 700, a planetary system 100 light-years away in the constellation Dorado, is home to TOI 700 d, the first Earth-size habitable-zone planet discovered by NASA’s Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite. Credit: NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
This illustration of TOI 700 d is based on several simulated environments for an ocean-covered version of the planet. Credit: NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
A schematic of the planets around the nearby M dwarf star TOI-700, discovered by TESS. The third (the farthest planet from the star), TOI-700d, lies within the star’s habitable zone (shown in green). Using the IRAC camera on Spitzer, the team refined the planet’s mass as 2.1 Earth-masses and 1.14 Earth-radii. (The scale shows 0.2 astronomical units; AU being the average Earth-Sun distance.) Credit: Rodriguez et al 2020
Happening on Twitter
Astronomers discovered a "rogue" planet smaller than Earth, free-floating through the Milky Way because it isn't ca… https://t.co/nGEdg1E37g IGN Fri Oct 30 03:03:05 +0000 2020
Wrote about rogue planets—cold, sunless worlds—"where the nightlife never ends": https://t.co/EhyFKchcfa marinakoren (from Washington, D.C. / The Milky Way) Thu Oct 29 18:33:09 +0000 2020
Ploonets are a newly-predicated class of orphaned moons that have been ejected from their planets and now orbit the… https://t.co/wXa85AmcQL AstronomyMag (from Our tiny corner of the cosmos) Wed Oct 28 09:30:11 +0000 2020
No comments:
Post a Comment