
The THYME collaboration aims to identify planets transiting stars in nearby, young, coeval populations. To date, the project has detected three extrasolar planetary systems and the finding of another one is reported in a recently published paper. The team, led by Benjamin M. Tofflemire of the University of Texas at Austin, have identified a transit signal in the light curve of the star HD 110082 (or TOI-1098). The planetary nature of this signal was confirmed by follow-up observations.
Many things are taking place:
Scientists think they've spotted another planet orbiting a nearby star – BGR

As The Guardian reports, researchers have spotted something in surveys of Alpha Centauri A — one of the two Sun-like stars in the system — that looks a whole lot like a planet. At a distance of just over 4 light-years from Earth, the system is right next door, but spotting something as tiny as a planet is still a major challenge. Put simply, the astronomers aren’t sure it’s a planet… but it could be.
Today's Top Deal Special coupon slashes 20% off KN95 masks that Amazon shoppers are obsessed with List Price: $26.99 Price: $21.59 You Save: $5.40 (20%) Available from Amazon, BGR may receive a commission Buy Now Coupon Code: CIGHI6XM Available from Amazon BGR may receive a commission
Satellite Database Update: More than 3,300 Active Satellites Orbiting the Earth - Union

It's a pretty challenging pace for our intrepid Database researcher, Teri Grimwood. Besides keeping on top of the 28 pieces of data for each of these satellites, Teri keeps an eye on what she sees as important and interesting trends. Here are some of those:
Following up from our post in May , the One Web story continues to evolve. In July, 2020 OneWeb was acquired by a partnership between the British government and Bharti Global, bidding together to purchase the bankrupt mega-constellation startup and return it to operations.
A Readily Implemented Atmosphere Sustainability Constraint for Terrestrial Exoplanets Orbiting
An ensemble of 1,771 confirmed exoplanets by the NASA Exoplanet Archive plotted on a diagram of stellar mass vs. astrocentric distance. We restrict the analysis to stars less or equally massive to the Sun while exoplanets shown have a confirmed orbital semi-major axis. Inner and outer HZ limits are indicated by solid lines enclosing the pink-shaded HZ area, while the black and gray dashed lines indicate internal and potential external tidal-locking limits, respectively.
Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs), spawn by magnetically active, superflare-triggering dwarf stars, pose a direct threat to the habitability of terrestrial exoplanets as they can deprive them from their atmospheres. Here we develop a readily implementable atmosphere sustainability constraint for terrestrial exoplanets orbiting active dwarfs, relying on the magnetospheric compression caused by CME impacts.
Not to change the topic here:
Astronomers discover trio of young planets orbiting a teenage sun | Sandhills Express

Floating in a stream of young stars, astronomers have spotted a trio of neighboring planets similar to Earth, orbiting a much younger version of our own sun.
The system is located in a newly-discovered Pisces-Eridanus stellar stream, which is less than 3% the age of our solar system, stretching across one-third of the sky. These so-called rivers of stars form when the gravity of our galaxy, the Milky Way, rips apart clusters of stars and dwarf galaxies, forming an elongated grouping that continues to disperse into a stream over time.
Young star, orbiting exoplanets discovered in a 'river of stars' using TESS, Spitzer data-
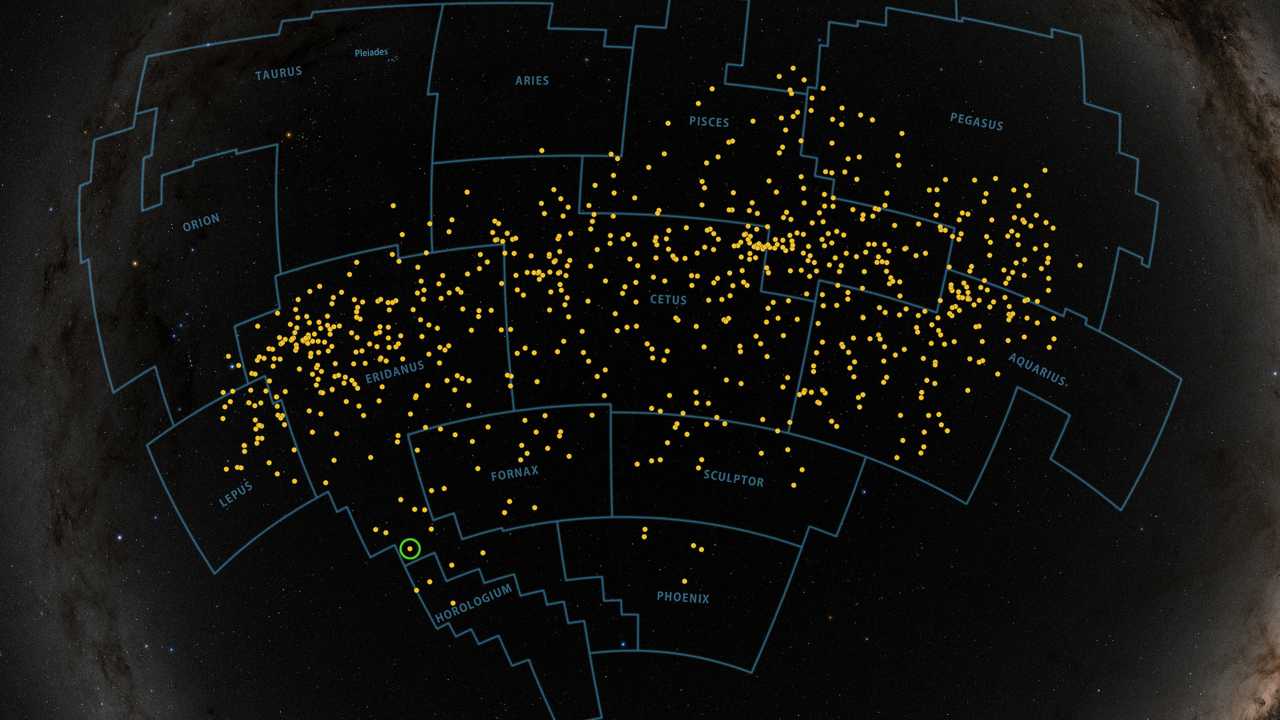
Astronomers have spotted a young star called TOI 451 that has three hot planets in orbit around it. The astronomers spotted the sun using NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS). The young star has a lot in common with our sun, according a NASA statement of the discovery. However, considering our sun's age is roughly 4.6 billion years old, the star TOI 451 is relatively younger, at 120 million years old.
All three planets that orbit TOI 451 sit very close to the star, according to the statement. This means that the planets are hot, with temperatures ranging from 2,200 °F (innermost planet) to 840 °F (outermost). The system also has a pair of companion stars that orbit far beyond the planets.
China's Tianwen-1 mission is now orbiting Mars ahead of landing | New Scientist

Reaching orbit is just the first step of the Tianwen-1 mission, which took off from the Wenchang launch site in Hainan, China, on 23 July last year. The spacecraft has three parts: an orbiter, a lander and a rover.
Now that the craft is safely circling Mars, the next step is to start the preparations for sending the lander to the surface. Scientists have selected a site for this in Utopia Planitia, the same region where NASA's Viking 2 lander touched down in 1976. Tianwen-1 will take pictures of the area from orbit to make sure conditions are safe.
Astronomers detect residue of Earth-like planets orbiting four dwarf stars in deep space

Scientists have long searched for planets with features similar to that of Earth, but so far haven't found a single one except for Mars, which obviously was much easier to detect given that we orbit the same solar system next to each other. However, astronomers from the University of Warwick may have found remnants of planets resembling Earth.
Scientists say these planets may have existed billions of years ago when the universe was still in its early phase. Scientists detected traces of sodium and calcium on the remains of the now-vanished planets. They also found the outer layers containing up to 3,00,000 gigatonnes of rocky debris, including 3,000 gigatonnes of potassium and 60 gigatonnes of lithium.
No comments:
Post a Comment