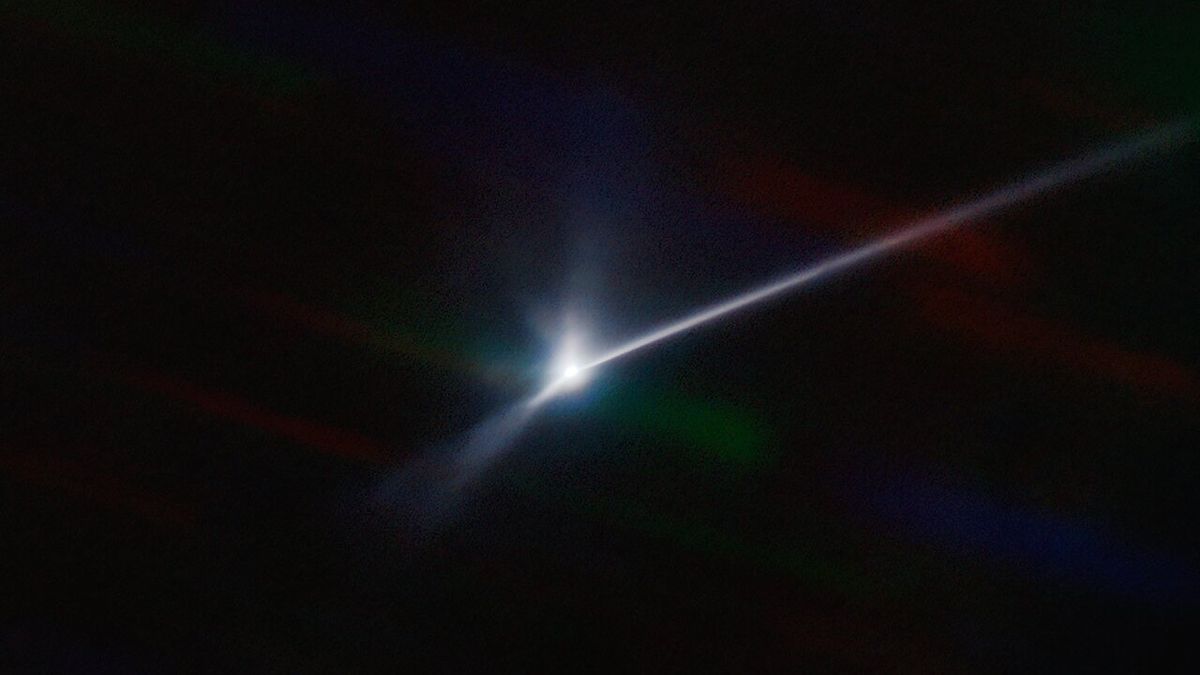

A new stunning image shows that two days after NASA's Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) spacecraft slammed into the asteroid Dimorphos, the space rock had grown a tail of glowing debris extending thousands of miles.
The comet-like tail is made of dust and debris was blasted from the surface of Dimorphos, part of a double asteroid system, by the intentional impact of DART , the first mission designed to test whether such a collision could divert a hypothetical asteroid threatening to hit Earth .
Asteroid that wiped out the dinosaurs also triggered a global tsunami | CNN

Sign up for CNN's Wonder Theory science newsletter. Explore the universe with news on fascinating discoveries, scientific advancements and more .
When a city-size asteroid slammed into Earth 66 million years ago, it wiped out the dinosaurs – and sent a monster tsunami rippling around the planet, according to new research.
Incredible Telescope View Captures DART Asteroid Impact

"Something like this has never been done before, and we weren't entirely sure what to expect. It was an emotional moment for us as the footage came in," explains Marco Micheli, Astronomer at ESA's NEOCC.
Hera scans DART's impact crater. Credit: ESA – Science Office
As DART's mission ends, the work begins for astronomers and researchers around the globe.
Smacked asteroid's debris trail more than 6,000 miles long
/cloudfront-us-east-1.images.arcpublishing.com/gray/ZHSAXK5ZBVABLGIJAMJXRRTA3Q.png)
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. (AP) — The asteroid that got smacked by a NASA spacecraft is now being trailed by thousands of miles of debris from the impact.
Astronomers captured the scene millions of miles away with a telescope in Chile. Their remarkable observation two days after last month's planetary defense test was recently released a National Science Foundation lab in Arizona.
Asteroid slammed by NASA spacecraft has debris trail over 6,000 miles long
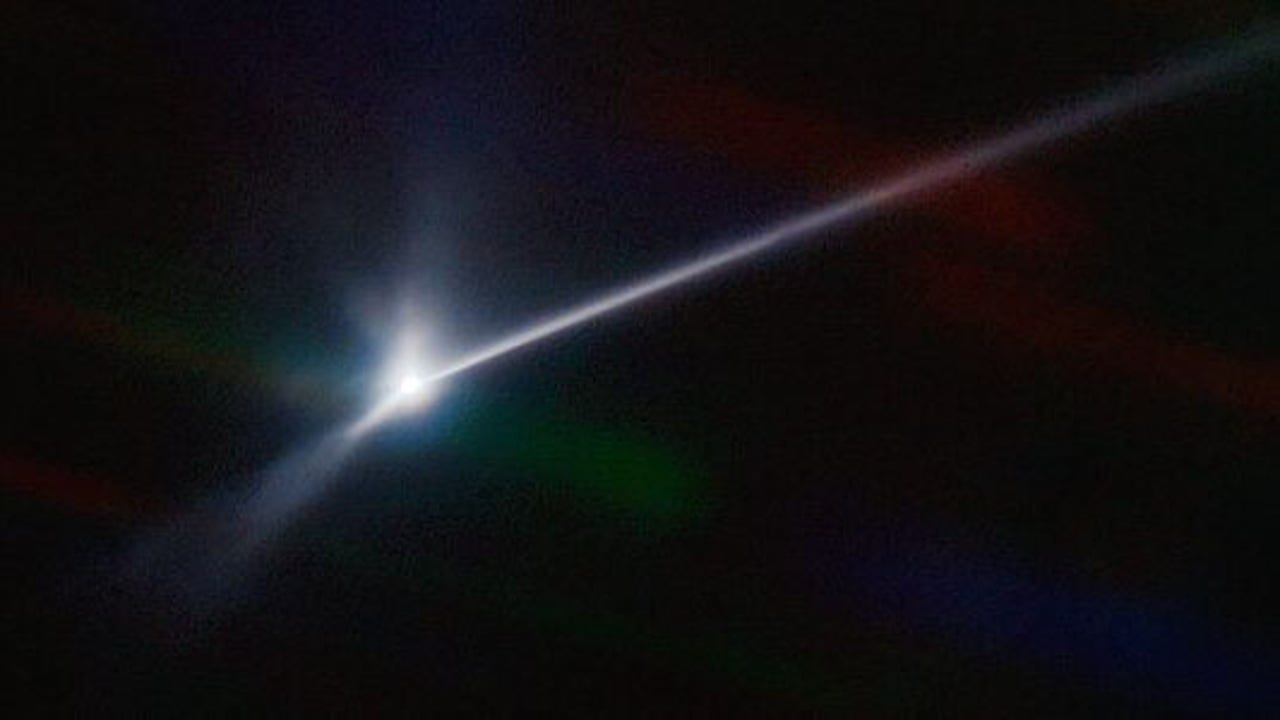

Astronomers using the NSF's NOIRLab's SOAR telescope in Chile captured the vast plume of dust and debris blasted from the surface of the asteroid Dimorphos by NASA's DART spacecraft when it impacted on Sept. 26, 2022. In this image, the more than 10,
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - The asteroid that got smacked by a NASA spacecraft is now being trailed by thousands of miles of debris from the impact.
Scientists identify potential source of 'shock-darkened' meteorites, with implications for ...

When the Chelyabinsk fireball exploded across Russian skies in 2013, it littered Earth with a relatively uncommon type of meteorite. What makes the Chelyabinsk meteorites and others like them special is their dark veins, created by a process called shock darkening.
In a new paper published in the Planetary Science Journal, University of Arizona scientists identified an asteroid named 1998 OR2 as one potential source of shock-darkened meteorites. The near-Earth asteroid is about 1 1/2 miles wide and made a close approach to Earth in April 2020.
Close encounters of the asteroid kind - ABC Radio National
Normally, when you build a $300 million spacecraft, you want it to last. Now imagine the exact opposite and you've got DART – a half-tonne spacecraft, purpose-built to be destroyed.
DART stands for Double Asteroid Redirection Test. "Double Asteroid" means two asteroids, closely orbiting each other. "Redirection" means changing the path of one of those asteroids, by hitting it head-on. And "Test" means it was a test.
Scientists Have Been Underestimating the Asteroid That Created the Biggest Known Crater on Earth - ...
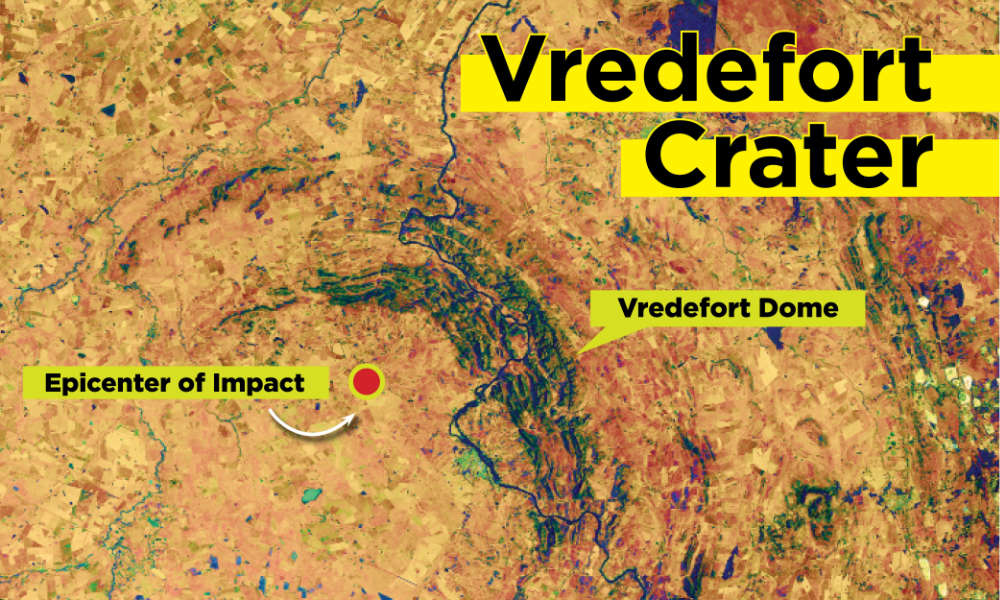
Ancient impacts played a powerful role in Earth’s complex history. On other Solar System bodies like the Moon or Mercury, the impact history is preserved on their surfaces because there’s nothing to erase it.
The most well-known giant impact on Earth is the Chicxulub impactor which wiped out the dinosaurs about 65 million years ago and cleared the way for mammals to become preeminent. But there’ve been other giant impacts, including one in South Africa.
After DART crash, asteroid Dimorphos sports a tail of debris thousands of miles long https://t.co/KcCSNglvbE https://t.co/IlcV9TsQ2b SPACEdotcom (from NYC) Tue Oct 04 15:05:14 +0000 2022
https://sypuber.page.link/reddcct
REDACTED ID. Click here.


No comments:
Post a Comment