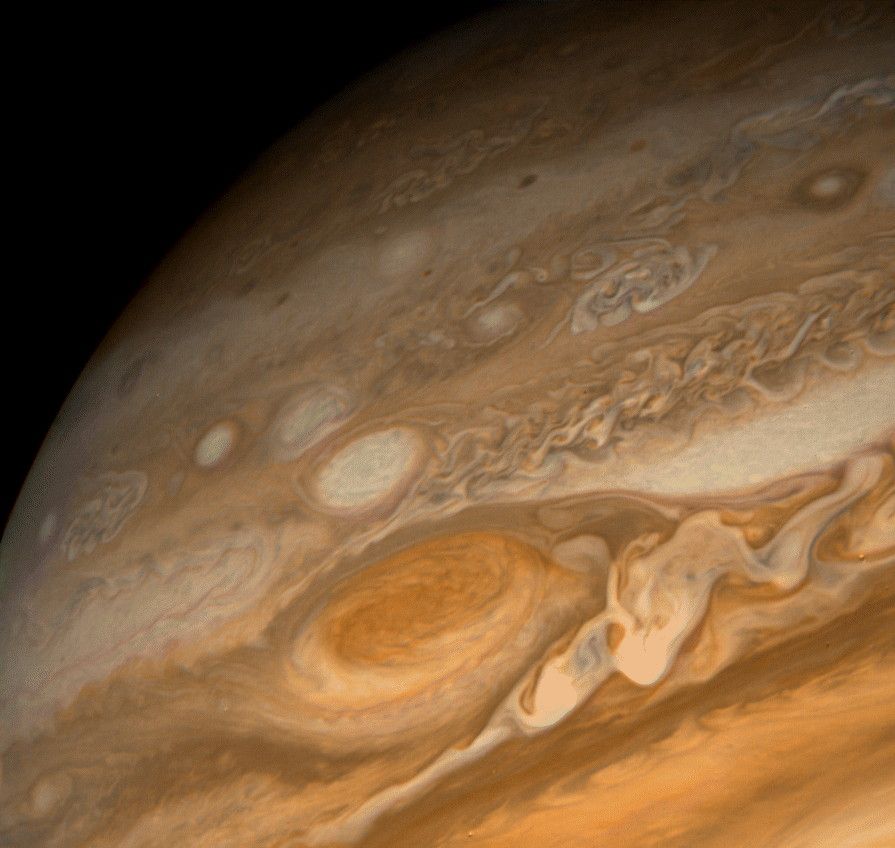

When you think of Jupiter , you might think of its massive size, or colorful bands of gases stretching across its face. Or you might think of the iconic storm, that huge, churning red hurricane twice the size of Earth that's remained a signature of our solar system's largest planet since for more than a century! Great Red Spot - Wikipedia en.wikipedia.org /wiki/ Great_Red_Spot The Great Red Spot is a persistent high-pressure region in the atmosphere of Jupiter, producing an anticyclonic storm , the largest in the Solar System, 22 degrees south of Jupiter's equator. It has been continuously observed since 1830. Observation history!! This is Jupiter's Great Red Spot and it has captivated humans for generations.
Jupiter's Great Red Spot was first observed in 1831 by amateur astronomer Samuel Heinrich Schwabe, so we know the storm has existed for at least 150 years! Jupiter Red Spot Facts | What Is Jupiter's Great Red Spot? www.popularmechanics.com /space/ solar -system/a28676462/ jupiter - great - red - spot It's one of the most iconic destinations in the solar system: Jupiter's Great Red Spot , moving around the planet like a wandering eye. But the famous storm is filled with plenty of mysteries.!! But it could be even older than that. Some astronomers speculate that, back in 1665, when astronomer Gian Domenico Cassini (the namesake for NASA's Cassini mission ) wrote about a "Permanent Storm," he was referring to the Great Red Spot.
* * *
This enhanced-color image of Jupiter's Great Red Spot was created by citizen scientist Jason Major using data from the JunoCam imager on NASA's Juno spacecraft.
Quite a lot has been going on:
What Makes a Planet and How Many Are There in Our Solar System?

What makes a space object a planet? How many are there actually in our solar system? Let's find out.
How many planets are there in our solar system? 9? 8? 12? More? The answer might actually surprise you.
Here we explore the answer to this apparently simple question and take a quick tour of the main primary planets of our home solar system.
* * *
What is a planet? An enormous chunk of stuff (rock or gas), roughly spheroidal in shape that orbits a star and may or may not have a moon, right?
While this is in part true, there are some issues with such a simple definition. What about asteroids? When does an object become large enough to be considered a planet?
Why are Venus and Mercury planets (according to current classifications) but not Pluto? As it turns out, the reasons are pretty straight forward.
Pressure at the Edge of the Solar System Is Far Higher Than Expected, Scientists Discover
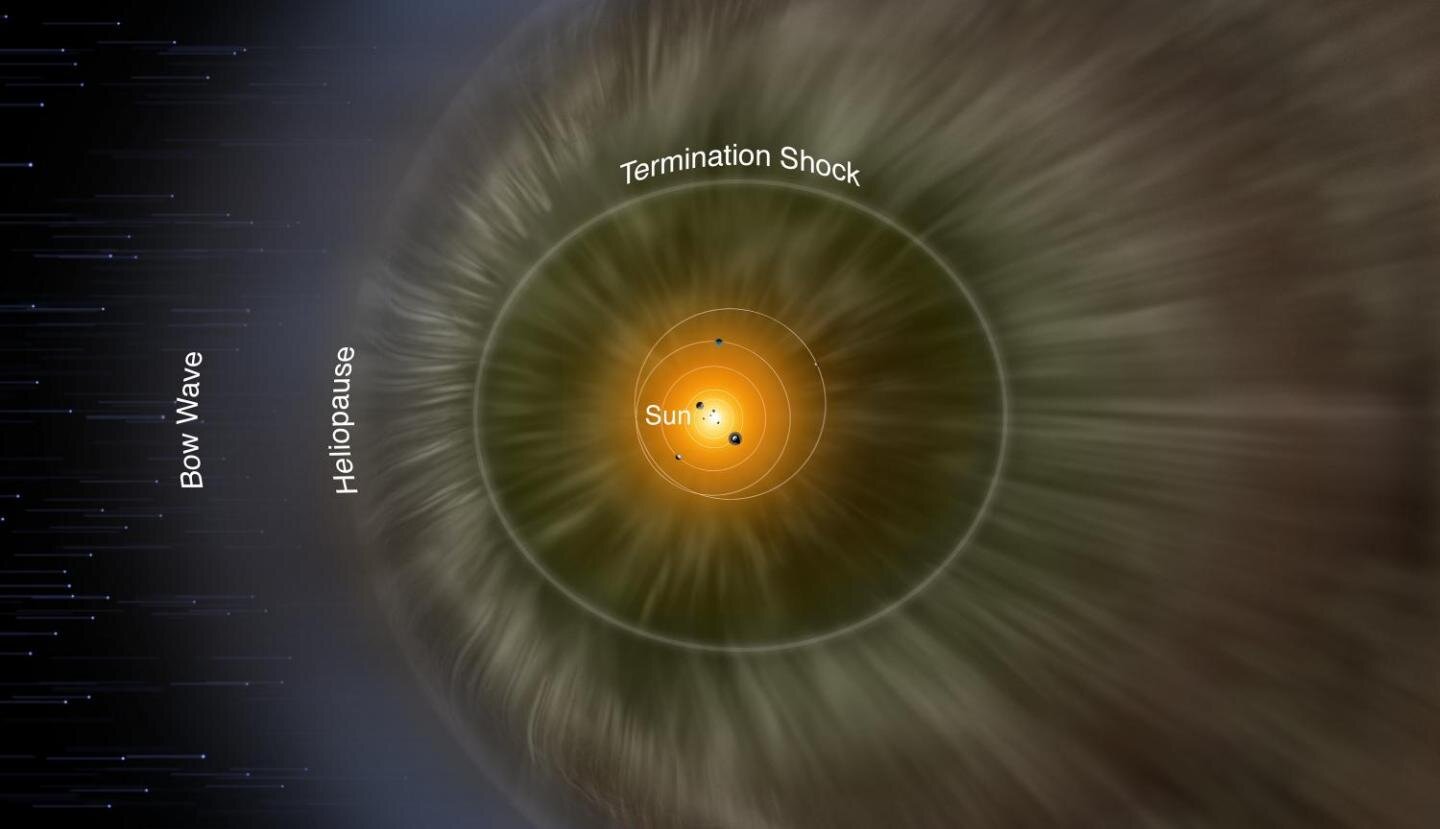
Scientists have found that the pressure at the edge of the solar system is greater than expected after analyzing data collected by NASA's Voyager spacecraft—the only objects to have traveled to interstellar space, where the sun's magnetic field no longer has influence over the environment.
The edge of the solar system is a poorly understood region of space given its distance from Earth and the difficulty of conducting observations there! Jupiter's Great Red Spot, Spotted | NASA Solar System ...solarsystem.nasa.gov /res our ces/857/ jupiters - great - red - spot - spot ted/?category=...Jupiter's Great Red Spot , Spotted . At the time the images were taken, the spacecraft was 15,379 miles (24,749 kilometers) to 30,633 miles (49,299 kilometers) from the tops of the clouds of the planet at a southern latitude spanning 43.2 to 62.1 degrees. Citizen scientists Gerald Eichstädt and Seán Doran processed this image using data from the JunoCam imager.!! But a study published in The Astrophysical Journal is helping to cast new light on the dynamics of this mysterious zone.
In our solar system, the solar wind—a constant flow of charged particles streaming out of the sun—inflates a bubble in the surrounding interstellar material! Is Jupiter's Great Red Spot disintegrating? | Space | EarthSky earthsky.org /space/is- jupiters - great - red - spot -disintegrating Jupiter's Great Red Spot is a giant storm , the largest known in our solar system. It's been seen through earthly telescopes for more than 300 years. Lately, it's been showing signs of breaking apart.!! This bubble is known as the "heliosphere" and it represents the extent of our star's magnetic influence.
A Faux Saturn Moon Titan on Earth Could Solve Solar System Mystery | Space

Big, schmancy compounds keep popping up all over the solar system , and new research may help clear up confusion about how they form in so many places.
"These dunes are pretty large," study senior author Ralf Kaiser, a chemist at the University of Hawaii at Manoa, told Space.com, nearly as tall as the Great Pyramid in Egypt, he added. "If you want to understand the carbon and hydrocarbon cycle and the processes of hydrocarbons on Titan, it's really important to understand, of course, where the dominant source of carbon comes from."
* * *
On Titan, there's a straightforward mechanism that scientists know likely builds polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: These large molecules can form in the moon's thick atmosphere and settle down to the surface! Probing the Secrets of Jupiter's Great Red Spot - ThoughtCo www.thoughtco.com/ jupiter - great - red - spot -4156733 Jupiter's Great Red Spot is the most massive and highly studied storm in the solar system. It is larger than Earth and is stronger than any hurricane known.!! But the same family of compounds has been found on plenty of worlds that boast no such atmosphere, like the dwarf planets Pluto and Ceres and the Kuiper Belt object Makemake .
Other things to check out:
Comet from another Solar System looks a lot like our own | Ars Technica

Interactions among the small bodies of our Solar System are expected to hurl small objects out into interstellar space with some regularity, and the frequency was probably much higher early in the system's history. Given that the same thing almost certainly happens at exosolar systems—and we now know there are a lot of those—it's likely that the vast volume of interstellar space is lightly sprinkled with small objects, some of which may sporadically pass through our own Solar System. But up until very recently, we'd had no evidence of their existence.
That situation changed with the discovery of 'Oumuamua , a strange, cigar-shaped body that was the first confirmed exosolar visitor. But 'Oumuamua was so strange that it set some astronomers speculating that it could be an alien craft . Earlier this year, however, scientists spotted a second potential exosolar visitor , and this one looked a lot like a comet. Now, the first data on the object, 2I/Borisov, is in, and it's clearly exosolar in origin but looks so much like our existing comets that we might not have realized where it was from if we didn't have a good grip on its orbit.
Visitors from deep space are buzzing our solar system. The race is on to explore them.

Two years ago, an automated telescope in Hawaii detected 'Oumuamua , the first known object from interstellar space observed passing through our solar system. Then in August, an amateur astronomer in Crimea found a second interstellar visitor, 2I/Borisov, suggesting that such objects come our way on a regular basis.
Now, scientists are eagerly developing plans to explore these messengers from afar and to learn their secrets.
For now, answers are trickling in slowly from observatories on the ground and in orbit around Earth, including an intriguing new image of Borisov just taken by the Hubble telescope . Come 2028, though, a European spacecraft called Comet Interceptor could be on its way to a brief encounter with another, as-yet-undetected interstellar object.
Hein and his colleagues have an even grander project in mind. They've drawn up plans for Project Lyra , a space probe that could travel fast enough to overtake either 'Oumuamua or Borisov (or another interstellar object) as it speeds its way out of the solar system, reaching either one by the mid-2040s.
Jupiter's Great Red Spot: Our Solar System's Most Famous Storm https://t.co/oTPkscBI4I https://t.co/Up21APwDNH SPACEdotcom (from NYC) Sat Oct 19 01:12:33 +0000 2019
Jupiter Hell 0.8.4 "Infernal Intellect" update is live! We're celebrating with a -20% discount on Steam, so it's a… https://t.co/JKMgfkAhYc epyoncf (from Wroclaw, Poland) Mon Oct 14 17:16:06 +0000 2019
No comments:
Post a Comment