
MEMPHIS, Tenn. (WMC) - Asteroids are small, rocky objects that orbit the sun. They are similar to planets but much smaller than planets. There are a lot of asteroids within our solar systems and most are located in an area between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter, which is called the asteroid belt.
Asteroids have been making close encounters to earth for millions of years. Most asteroids disintegrate in the earth's atmosphere.
Lately, there has been some speculation about an asteroid called 2018 VP1 that could hit around election day. The asteroid was discovered on November 3, 2018 at an observatory in Southern California. VP1 was discovered as a faint new "near-Earth asteroid" which is an object whose orbit can approach, or intersect, that of our planet.
Were you following this:
Astronomers Have Discovered a Surprise Asteroid Orbiting Closer to The Sun Than Venus
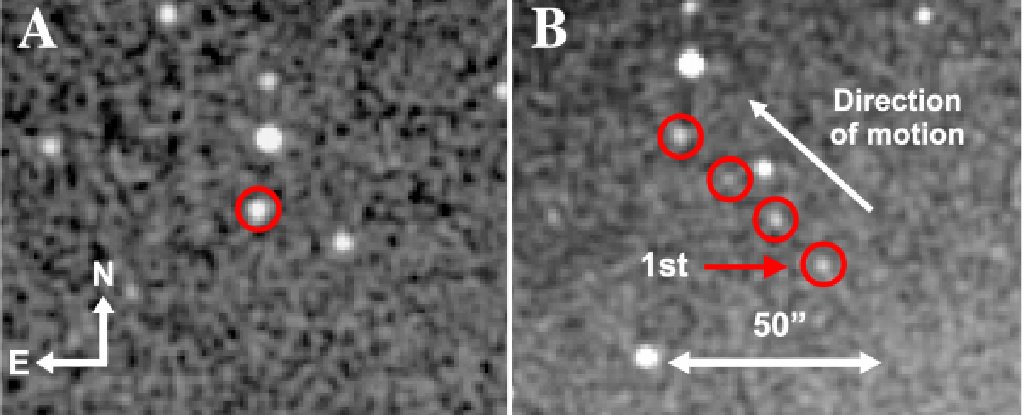
Astronomers have painstakingly built models of the asteroid population, and those models predict that there will be ~1 km sized asteroids that orbit closer to the Sun than Venus does. The problem is, nobody's been able to find one. Until now.
Astronomers working with the Zwicky Transient Facility say they've finally found one. But this one's bigger, at about 2 km. If its existence can be confirmed, then asteroid population models may have to be updated.
Asteroid 'bigger than London Bridge' to fly past Earth on Sept 17; all you need to know -

On September 17, while the new moon embraces the sky, a giant Asteroid 2014 QJ33 about the size of London Bridge will fly past the Earth. According to NASA's Centre for near-Earth Object Studies (CNEOS), the gigantic asteroid will come in close proximity of Earth and will pass through its orbit at a distance of 2.56 million kilometres, next week. Asteroid 2014 QJ33 is a near-Earth object ( NEO ) and is classified as the Apollo asteroid with a peak diameter of 110 metres.
* * *
[NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California prepares to launch Psyche that will explore metal-rich asteroids. Credit: NASA]
Mission set to collect sample from asteroid - Chinadaily.com.cn
China intends to carry out a mission to collect a sample from the smallest and closest "quasi-satellite" to Earth around 2025, said a key figure in the country's deep-space exploration program.
Zhang Rongqiao, chief designer of China's Mars exploration effort, said on Friday that Chinese space authorities have chosen the 2016 HO3, a small asteroid, as the target for the mission.
The preliminary idea is to use a large carrier rocket to send a probe, which will consist of two parts-an orbiter and a re-entry module, toward the asteroid, he said.
In case you are keeping track:
Asteroid news: Space rock has 'very close but safe encounter' with Earth | Science |

A space rock known as 2020 RZ6 swung by our planet closer to us than the orbit of the Moon on the evening of September 17. The asteroid, which is up to 27 metres in length, flew by our planet at a distance of 340,000 kilometres, or 88 percent the distance of the Moon.
* * *
Shortly after the image passed, the Virtual Telescope Project said: "Minutes ago, the near-Earth asteroid 2020 RZ6 had a very close, but safe, approach with our planet, reaching a minimum distance from the Earth of about 340000 km, 0.88 times the average distance of the Moon.
Asteroid Watch 2020: ESA, Germany's OHB To Build Spacecraft For Planetary Defense Mission

Humanity's first attempt at deflecting an asteroid from its path by ramming a spacecraft into it will involve a joint effort by American and European to see if potentially devastating collisions with Earth can be averted.
The test-run of a pioneering planetary defense mission is called AIDA (Asteroid Impact and Deflection Assessment) involving an American and European spacecraft. The impactor spacecraft called DART (Double Asteroid Redirection Test) will attempt to slam into a tiny moonlet called Dimorphos, which orbits the asteroid 65803 Didymos, in 2022.
Next target asteroid picked for Japan's Hayabusa2 probe | The Japan Times

The unmanned Hayabusa2 probe will explore the asteroid 1998KY26 after completing its current mission of delivering a capsule believed to be containing samples of sand from the asteroid Ryugu to Earth, the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) said Tuesday.
The probe is expected to reach 1998KY26, which is traveling between Earth and Mars, in July 2031. The asteroid is only about 30 meters in diameter, smaller than the roughly 900 meter diameter of Ryugu, and rotates about every 10 minutes, compared to about seven hours for Ryugu.
Mars smallsat mission bumped from launch - SpaceNews
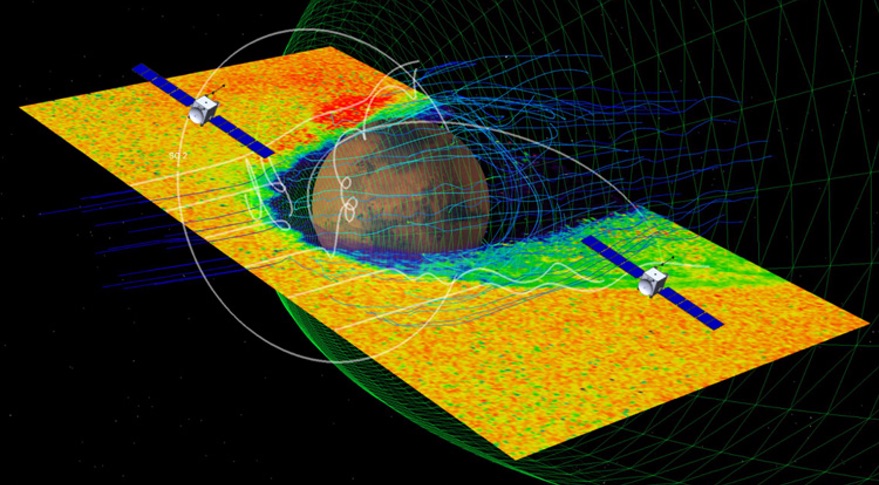
WASHINGTON — A smallsat mission to study the atmosphere of Mars is looking for a new ride after being removed as a secondary payload on the launch of a NASA asteroid mission.
The Escape and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers, or EscaPADE, mission, was one of three smallsat missions selected by NASA in 2019 for initial studies as part of the agency's Small Innovative Missions for Planetary Exploration (SIMPLEx) program. EscaPADE features twin spacecraft that would orbit Mars to study how the planet's atmosphere interacts with the solar wind, and how those processes lead to the escape of gases from the atmosphere.
Happening on Twitter
Why Can't We Talk About George Soros's Plan To Remake America? Great breakdown by @robbystarbuck. cc:… https://t.co/1y1zmLP8Vx johncardillo (from Florida ) Sat Sep 19 14:09:25 +0000 2020
We launched a Podcast! Give a listen as @markellislive and I have a cinematic therapy session each week and breakd… https://t.co/nYVsVbIUES THATJacqueline (from ATX - LA) Thu Sep 17 16:39:31 +0000 2020
Just last week, SLC police shot an unarmed, 13-year-old autistic boy having a breakdown because his mother was retu… https://t.co/DXtXaYfu61 AdrienneLaw (from Los Angeles, CA) Sun Sep 13 23:25:47 +0000 2020
No comments:
Post a Comment