
Astronomers have spotted a possible searing-hot planet orbiting Vega , one of the brightest and most famous stars in the sky.
The candidate alien planet , which still needs to be confirmed by follow-up observations or analyses, is roughly the size of Neptune and lies very close to Vega. It takes only 2.5 Earth days for the purported planet to make a single orbit around its sun.
Thanks to that proximity, the candidate planet's surface temperature is probably around 5,390 degrees Fahrenheit (2,976 degrees Celsius), researchers calculated. That would make it the second-hottest planet known, if it does indeed exist. (The hottest, KELT-9b , is a whopping 7,800 degrees Fahrenheit, or 4,300 degrees C.)
Other things to check out:
Did You Know Some Planets Are Hotter Than Stars? - The Wire Science

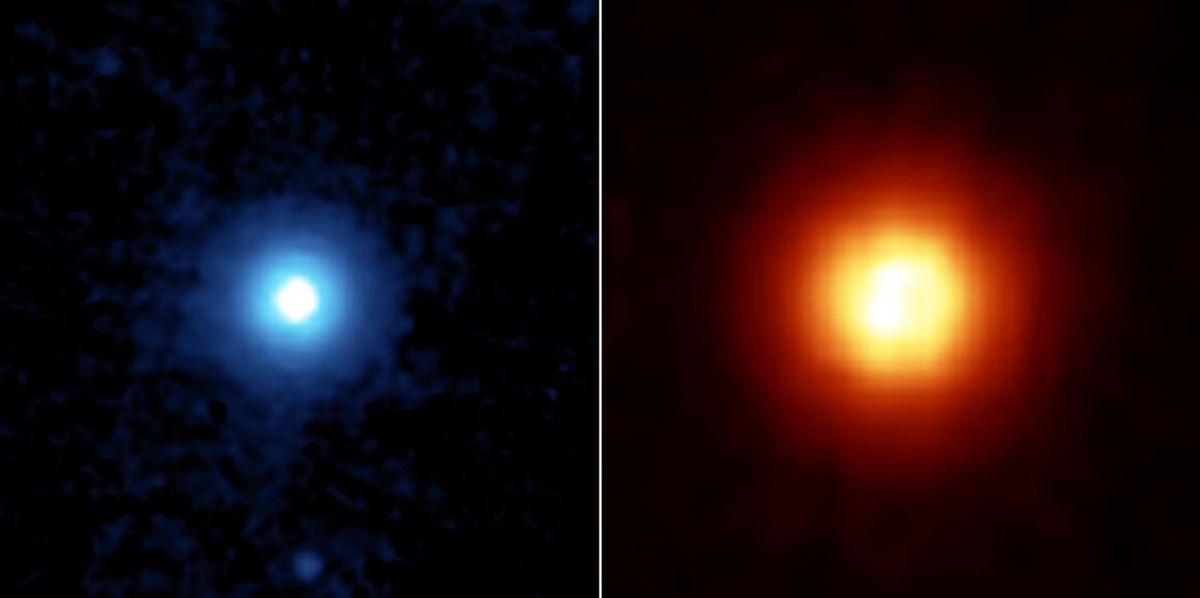
Artist’s impression of exoplanet KELT-9b orbiting its host star, KELT-9. Photo: NASA/Wikimedia Commons
Until the early 2000s, the only known planets were located in our own neighbourhood, the solar system. They broadly form two categories: the small rocky planets in the inner solar system and the cold gaseous planets located in the outer part. With the discovery of exoplanets, planets orbiting stars other than the sun, additional classes of planets were discovered and a new picture started to emerge . Our solar system is by no means typical.
This strange lava-rich alien planet is making itself a new atmosphere | Space
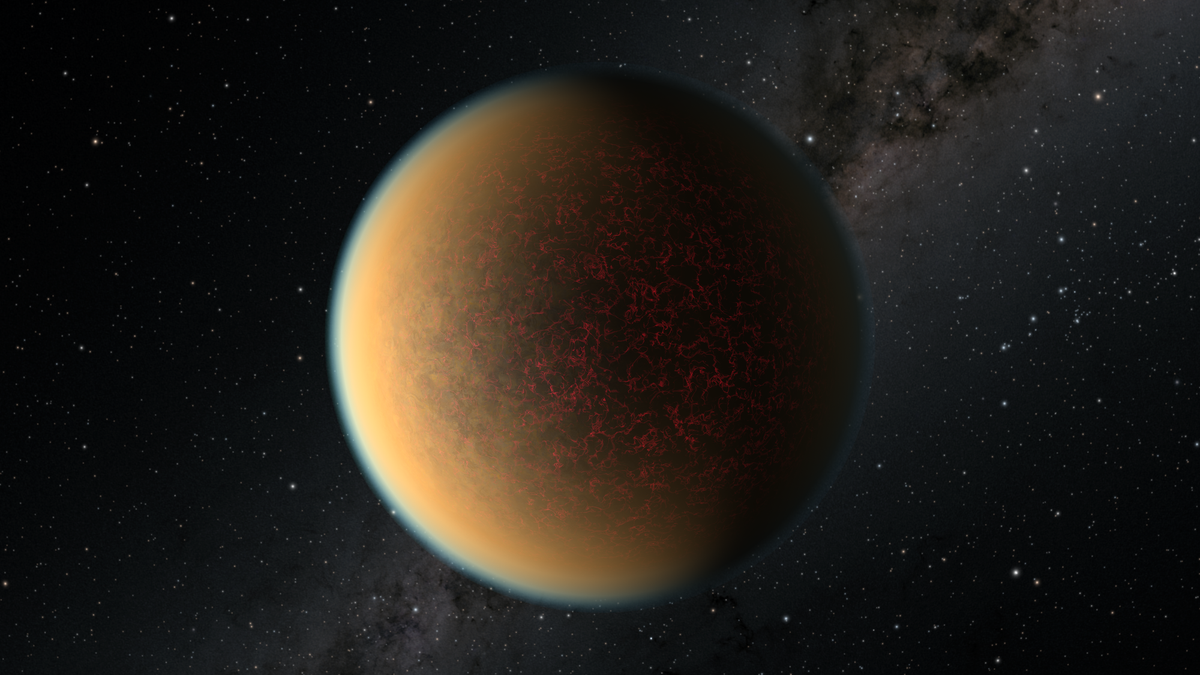
Scientists think they've spied an alien world that lost its atmosphere — then conjured itself a new one.
That's according to a new analysis of Hubble Space Telescope observations gathered in 2017 of a planet dubbed GJ 1132 b. The world tightly orbits a red dwarf star located about 41 light-years from Earth, completing one circle every 1.5 Earth days and soaking up lots of stellar radiation in the process. And now, scientists think they see signs of a secondary atmosphere, one that was born of the exoplanet itself long after the planet formed.
A planet lost its previous atmosphere, but has formed a new one | 9news.com

Scientists believe that an exoplanet with a similar size and density as Earth may have lost its atmosphere and then regenerated another one. This would mark the first time that researchers have found an exoplanet which has a regenerated secondary atmosphere.
The planet, which orbits a star outside of our solar system, was dubbed by scientists as GJ 1132. It is believed to have evolved from a gaseous state to a rocky one the size of Earth.
And here's another article:
Hubble Finds Earth-Sized Planet That May Be on Its Second Atmosphere
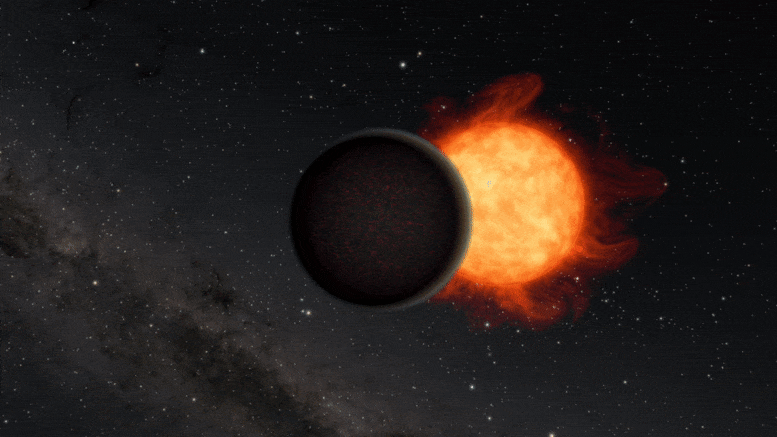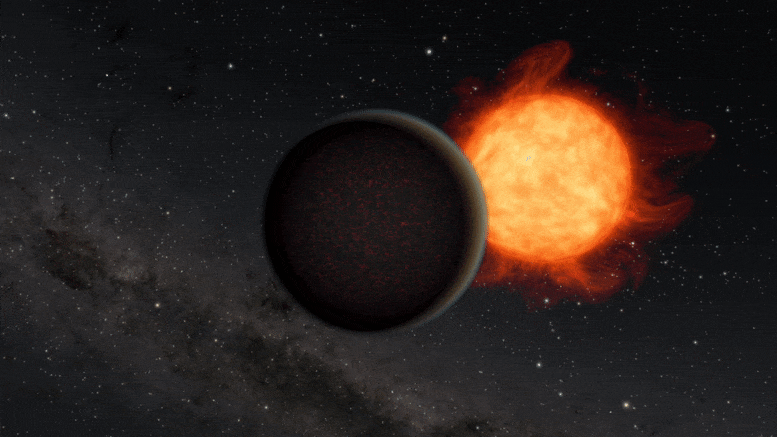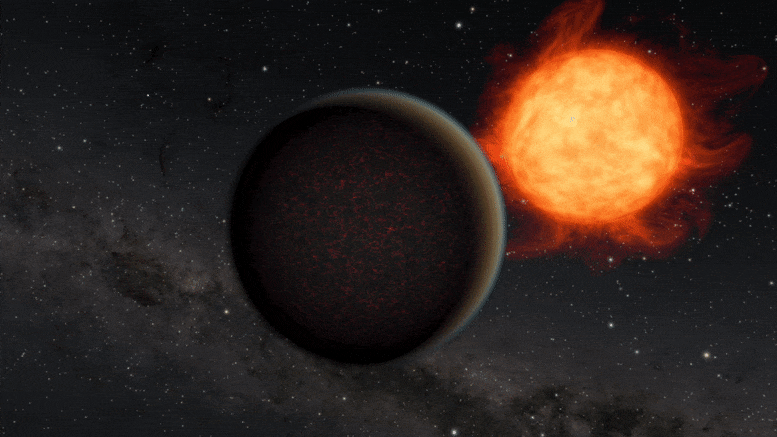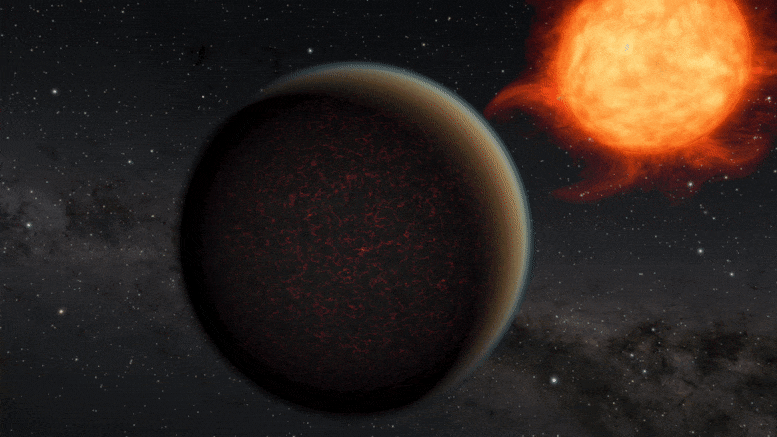
Scientists using NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope have found evidence that a planet orbiting a distant star may have lost its atmosphere but gained a second one through volcanic activity.
The planet, GJ 1132 b, is hypothesized to have begun as a gaseous world with a thick hydrogen blanket of atmosphere. Starting out at several times the diameter of Earth, this so-called “sub-Neptune” is believed to have quickly lost its primordial hydrogen and helium atmosphere due to the intense radiation of the hot, young star it orbits. In a short period of time, such a planet would be stripped down to a bare core about the size of Earth. That’s when things got interesting.
Researchers think a planet lost its original atmosphere, built a new one | Ars Technica

The atmosphere most planets start with is often not the same as the one they end up with. Most of the gas present at the formation of a solar system will be hydrogen and helium. But a look through the rocky planets of our Solar System shows three very different atmospheres (and one very tenuous one), with hydrogen and helium being relatively minor components.
This week, an international team of astronomers reported finding an atmosphere on a planet where one wouldn't be expected to exist. And the astronomers suggest that it's actually the planet's second atmosphere, generated by volcanic activity after the first was boiled off early in the planet's history.
This planet is hotter than 80 per cent of stars in the universe, Science News | wionews.com

(Image- NASA/ Wikimedia Commons) Artist's representation of the planet revolving around its star Photograph:( Others )
Can you imagine a space body almost hot as our Sun all the while being a 'planet'? Well, there are such planets
But universe, as infinite it is, has ways to surprise our minds and set ideas we tend to have about it.
* * *
Kelt-9 b is a gaseous planet and it is 1.8 times bigger than Jupiter, the biggest planet in our solar system. It revolves around its star that is twice as hot as the Sun. In addition, Kelt-9 b has a very very short radius of revolution. It means that it revolves around its star in a very close orbit that is smaller even than that of Mercury in our Solar System.
Astronomers discover trio of young planets orbiting a teenage sun in a river of
Floating in a stream of young stars, astronomers have spotted a trio of neighboring planets similar to Earth, orbiting a much younger version of our own sun.
The system is located in a newly-discovered Pisces-Eridanus stellar stream, which is less than 3% the age of our solar system, stretching across one-third of the sky. These so-called rivers of stars form when the gravity of our galaxy, the Milky Way, rips apart clusters of stars and dwarf galaxies, forming an elongated grouping that continues to disperse into a stream over time.
Happening on Twitter
When I first landed in Beijing, I looked out the plane's window and thought it was snowing. No -- it was scorching… https://t.co/e8WmOOY5xc ezralevant (from Canada and the world) Mon Mar 15 01:33:27 +0000 2021
Social media is still buzzing over Cardi B and Megan Thee Stallion's scorching performance at the #Grammys https://t.co/WLiS7JTxXg JustJared (from New York City) Mon Mar 15 03:18:42 +0000 2021
What do you do if you start off life as a happy mini-Neptune-sized planet and your jerkwad host star blows off all… https://t.co/KMVVquvcxs BadAstronomer (from Boulder) Fri Mar 12 16:30:07 +0000 2021
We're back.... still scorching hot Alabama 57, Mississippi State 21 | 16:40 2nd H #RollTide |… https://t.co/h96azy5dI3 AlabamaMBB Fri Mar 12 18:17:53 +0000 2021
No comments:
Post a Comment