
A grand celestial reunion is due in Earth's skies throughout June. Sky-watchers will get a rare chance to see all the major planets in our solar system bunched together—with the moon joining the festivities, too, from June 17 to June 27.
This rare alignment includes the five planets easily spotted with the naked eye: Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn. Each is bright enough to be seen even in light-polluted city skies, with brilliant Venus being the brightest and Mercury the faintest.
Rare alignment of 5 planets to occur in late June | National News | tulsaworld.com

How Do Planets Form? - WorldAtlas
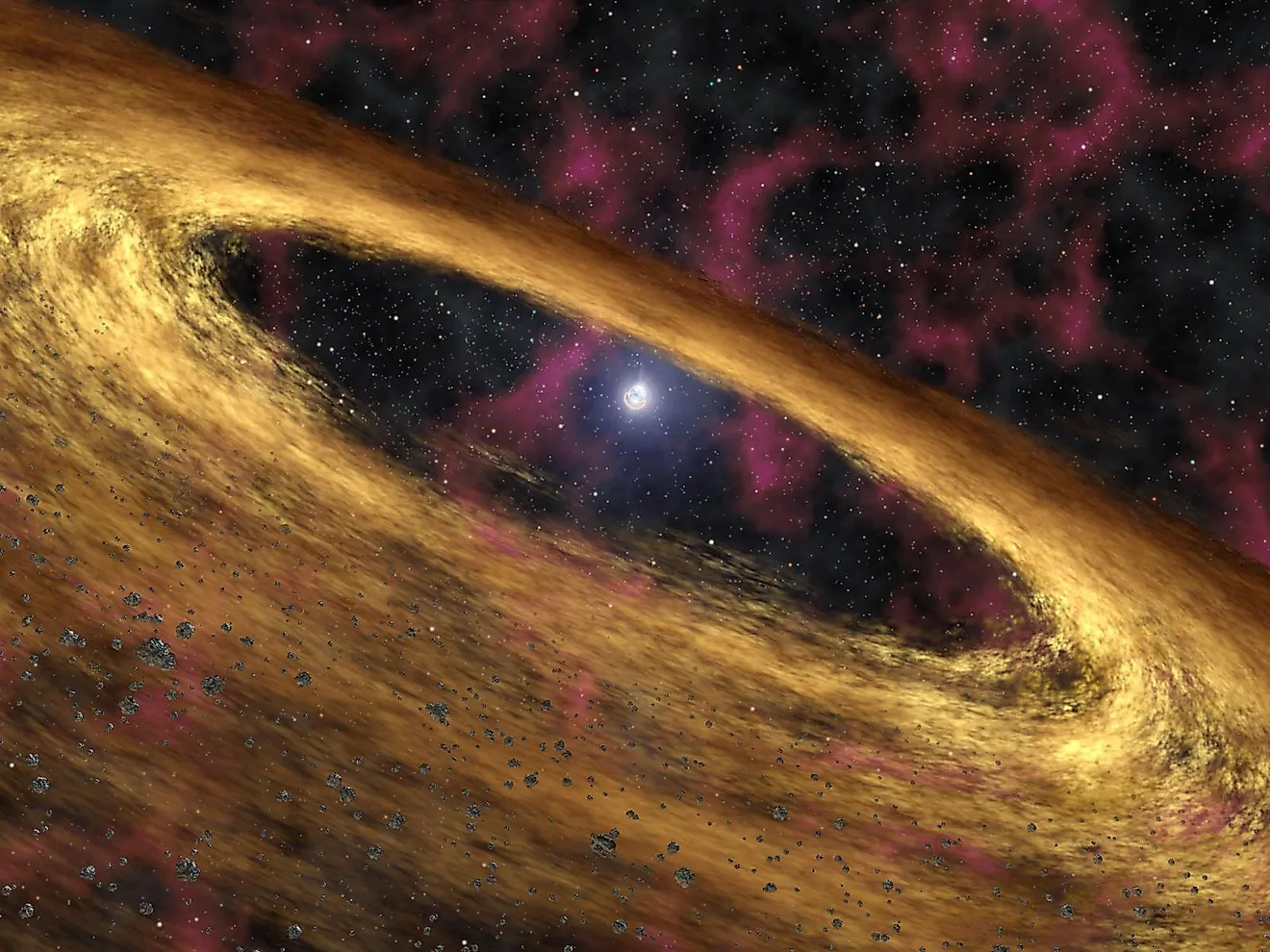

The higher core temperatures of massive stars means they can create a much higher diversity of heavy elements in their core compared to small mass stars. Many metals, such as magnesium and iron, come from high-mass stars.
If it were not for supernova explosions, the heavy elements within massive stars would have no way of being dispersed into space. Eventually, the very same material that once composed a massive star will be used to form an entirely new star with its own solar system.
How planets form depends on how big their star is, astronomers find | The Independent
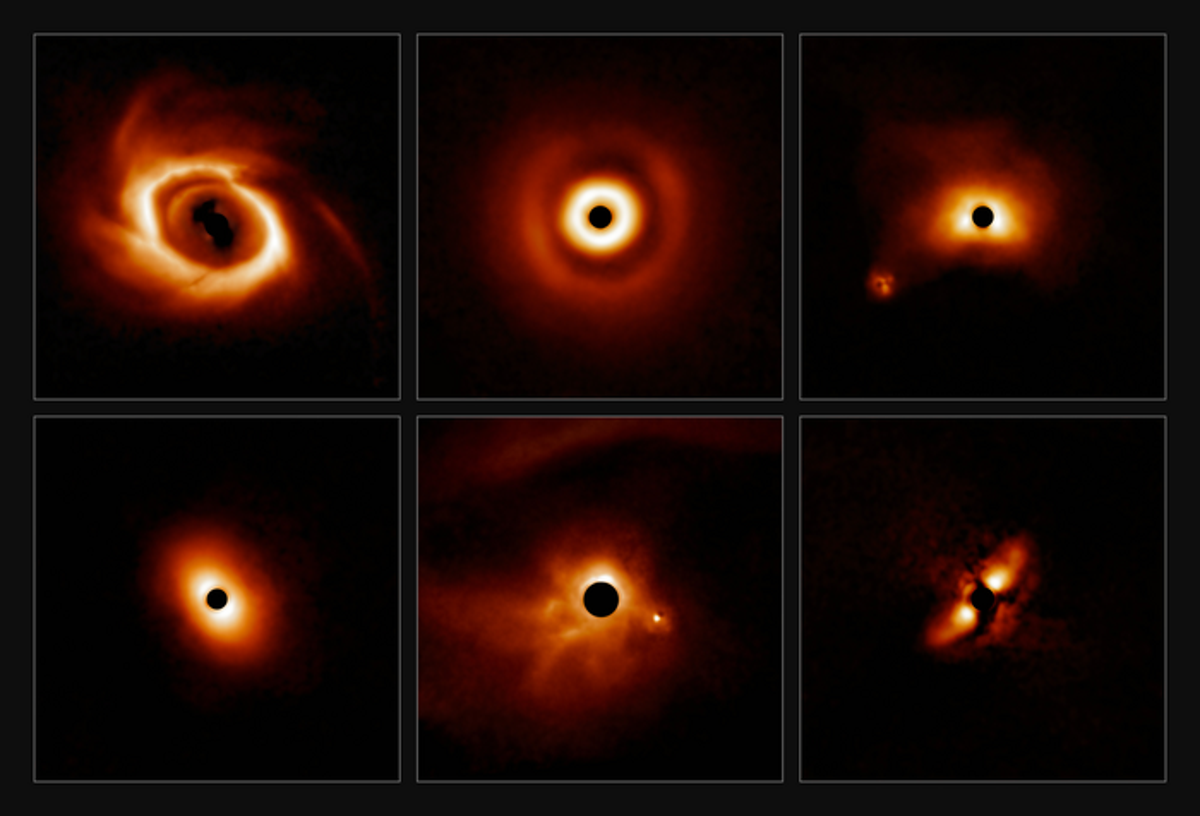

New research presented Wednesday at the 240th Meeting of the American Astronomical Society describes how researchers trained the Gemini telescope in Chile on more than 40 young, massive stars, revealing new information about how their size could impact planet formation.
The new findings suggest that the form and behavior of protoplanetary disks depends heavily on the size of the star at their center. For stars only somewhat more massive than our Sun, the disks broke into dusty rings. In contrast, disks of more massive stars were not ringed.
NASA Perseverance rover's pictures raise question: Can humanity be trusted with other planets?

At first glance, it may seem like a discarded packet of chips, so you may not think much of it, since it is only one piece of debris. However, the image has reignited concerns that space exploration risks 'contaminating' pristine other worlds and environments.
Should humanity at a time when we can barely control the pollution on our own planet, be trusted with alien planets?
Looking Skyward: The summer solstice and a rare alignment of the planets | CAI

In this edition of Looking Skyward, CAI's John Basile talks with Regina Jorgenson of the Maria Mitchell Observatory about the summer solstice. They also discuss the rare chance to see five planets at once in the late June sky.
Rapidly Expanding Black Hole Discovered using ANU's SkyMapper Telescope, Devours Planets | ...
Rare meteorite refines theory of Mars's formation | Popular Science

A one-of-a-kind meteorite from Mars has an unexpected chemistry that could refine scientists' models of how terrestrial planets form, according to a new study of the old space rock.
Chemical clues from this far-flung sample hint that Mars and Earth–often viewed as would-be twins because they are rocky worlds and solar system neighbors–were birthed in very different ways: Earth formed slowly, and Mars much faster.
Astronomers discover a multiplanet system nearby

Newswise — Astronomers at MIT and elsewhere have discovered a new multiplanet system within our galactic neighborhood that lies just 10 parsecs, or about 33 light-years, from Earth, making it one of the closest known multiplanet systems to our own.
At the heart of the system lies a small and cool M-dwarf star, named HD 260655, and astronomers have found that it hosts at least two terrestrial, Earth-sized planets.
If you miss this spectacle, you'll have to wait until 2040 to get another chance to see it https://t.co/nG6ro5qddG NatGeo (from Global) Thu Jun 16 14:09:00 +0000 2022
In June, five planets will move into a rare alignment, which will be visible from Earth. Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupi… https://t.co/v3PBSHuNbp CBSNews (from New York, NY) Wed Jun 08 20:30:00 +0000 2022
Army of the Alien Monkeys
Earth is nice. We want it.
We welcome your submission to us.
No comments:
Post a Comment