
PITTSBURGH (KDKA) – You may have heard about the full moon on 12/12 occurring at 12:12 a.m. by now. The timing of that full moon makes it a little special, but that is certainly not the only thing happening Wednesday night into Thursday.
The southern sky is going to have a whole lot going on, making for a night of “heavenly bodies” moving across the sky. If you stay up all night and find a good vantage point, you have the potential to see five planets and the full “Cold Moon” over the course of the night.
Many things are taking place:
Physicists May Have Just Solved a Fundamental Mystery of How Planets Form
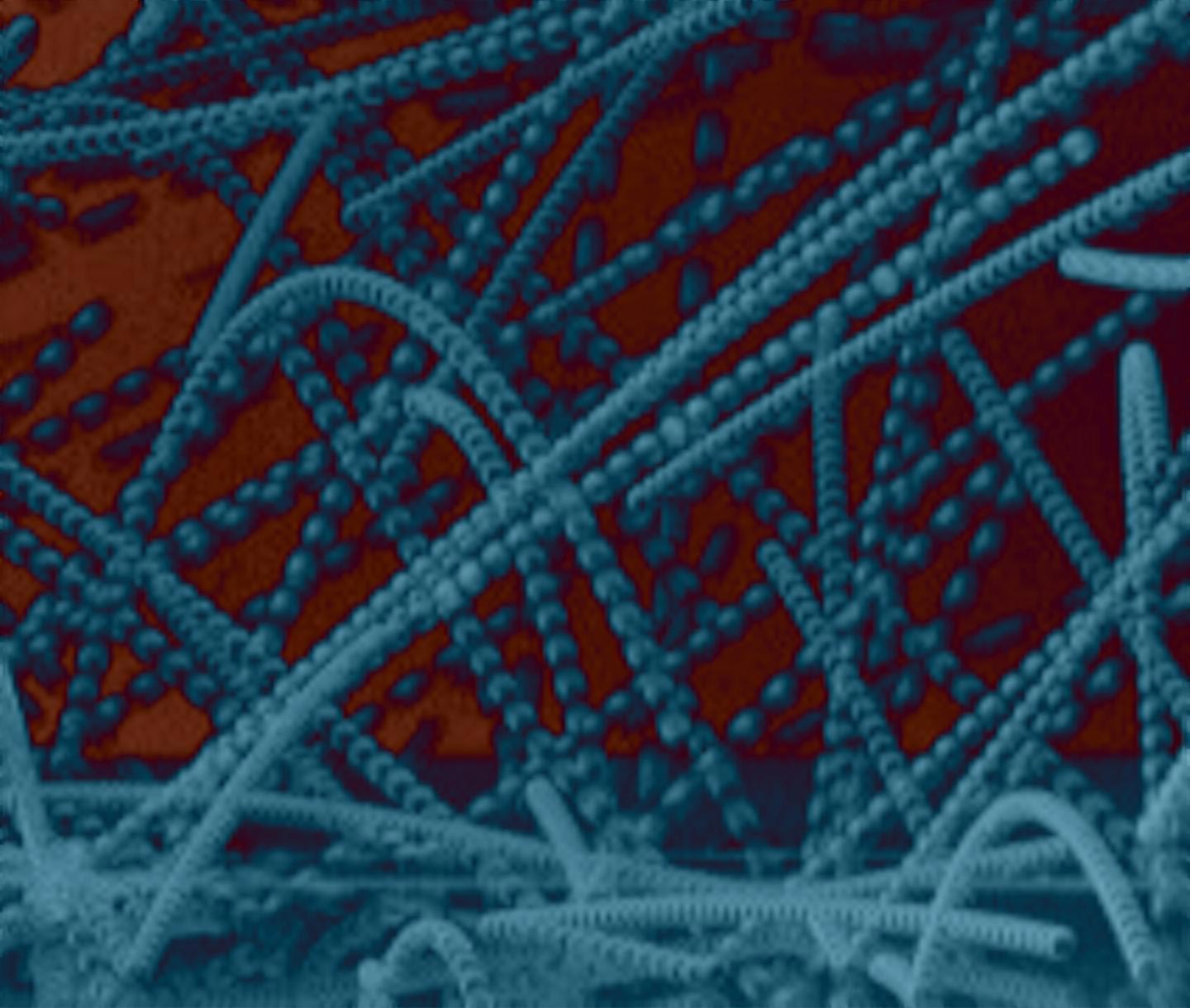
These are glass particles colliding in microgravity. Credit: Gerhard Wurm, Tobias Steinpilz, Jens Teiser, and Felix Jungmann
In homes, adhesion on contact can cause fine particles to form dust bunnies. Similarly, in outer space, adhesion causes dust particles to stick together. Large particles, however, can combine due to gravity — an essential process in forming asteroids and planets. But between these two extremes, how aggregates grow has largely been a mystery until now.
Planet four times the size of its star discovered - BBC Science Focus Magazine

Astronomers say the evidence for the distant planet comes in the form of a disc of gas created from its evaporating atmosphere. The Neptune-like planet is thought to be more than four times the size of the Earth-sized white dwarf star it orbits.
The giant planet orbits the star about once every 10 days, leaving a trail of gas comprised of hydrogen, oxygen and sulphur in its wake.
Until now, there has been no evidence of a planet that has survived a star's transition to a white dwarf , researchers say.
How dust comes together to form planets - Futurity

"We may have overcome a fundamental obstacle in understanding how planets form," says coauthor Troy Shinbrot. (Credit: Getty Images )
* * *
In homes, adhesion on contact can cause fine particles to form dust bunnies. Similarly in outer space, adhesion causes dust particles to stick together. Large particles, however, can combine due to gravity—an essential process in forming asteroids and planets. But between these two extremes, how aggregates grow has largely been a mystery until now.
Other things to check out:
Constraints on Aquatic Photosynthesis for Terrestrial Planets Around Other Stars - Astrobiology
Aquatic photosynthesis plays a major role in carbon fixation and O2 production on Earth. In this paper, we analyze the prospects for oxygenic photosynthesis in aquatic environments on Earth-analogs around F-, G-, K- and M-type stars.
Our analysis takes into account the spectral type of the host star, attenuation of light by aquatic organisms, and rates of respiration and photosynthesis. We study the compensation depth (ZCO) and the critical depth (ZCR), defined respectively as the locations where the net growth rates and vertically integrated net growth rates of photoautotrophs become zero.
Our planet is partly made of stardust from red giants - Futurity

They can also explain why the Earth contains more of this stardust than the asteroids or the planet Mars, which are farther from the sun.
Around 4.5 billion years ago, an interstellar molecular cloud collapsed. At its center, the sun formed; around that, a disc of gas and dust appeared, out of which the Earth and the other planets would form.
This thoroughly mixed interstellar material included exotic grains of dust. “Stardust that had formed around other suns,” explains Maria Schönbächler, a professor at the Institute of Geochemistry and Petrology at ETH Zurich. These dust grains only made up a small percentage of the entire dust mass and were distributed unevenly throughout the disc.
Brilliant Planetary Visualizations Will Rock Your World - Nerdist

Visualizing our solar system is one of those third-eye treats that never grows old. The Sun and its gravitationally bound planets, asteroids, etc. are in constant relative motion, and thinking about all of the different bodies swinging around each other (planets around the Sun, moons around the planets) conjures in the mind a seemingly endless dance against a backdrop of starry space. Speaking of which, Japan-based planetary scientist, Dr.
Oxygen-rich planets may be more common than we thought
![]()
The development of oxygen on Earth may not have come from external forces, researchers have found, with major implications for other planets.
'This could help us to better understand how a planet other than our own may become habitable'
– DR BENJAMIN MILLS
"Based on this work, it seems that oxygenated planets may be much more common than previously thought, because they do not require multiple – and very unlikely – biological advances, or chance happenings of tectonics."
Happening on Twitter
🪐 LOOK UP 🌕 Heavenly bodies are on the move tonight! You'll be able to spot five planets as well as the full moon t… https://t.co/eD3Wp6HNlp KDKA (from Pittsburgh, PA) Wed Dec 11 13:00:01 +0000 2019
5 planets will be visible (at various times), tonight, along with the 12/12 12:12 Full "Cold Moon". Read this arti… https://t.co/1lAulZUcOr RayPetelinWx (from Pittsburgh, PA) Wed Dec 11 18:05:30 +0000 2019

No comments:
Post a Comment